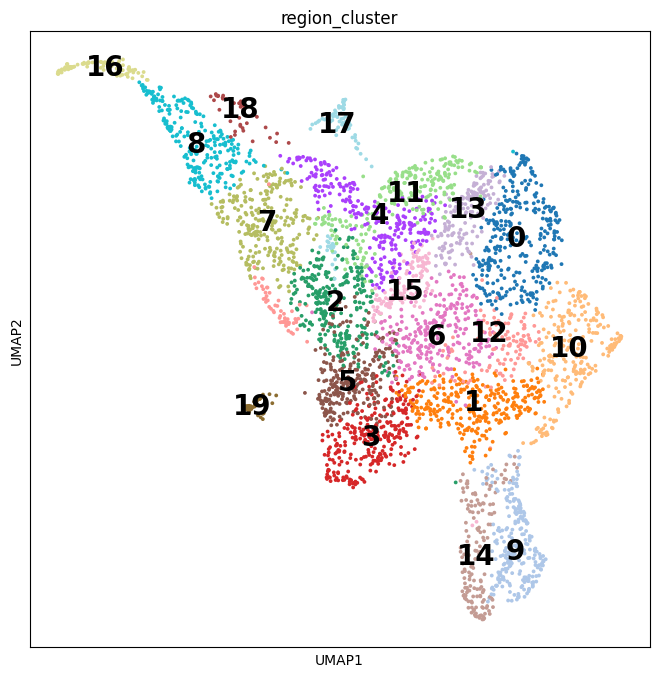
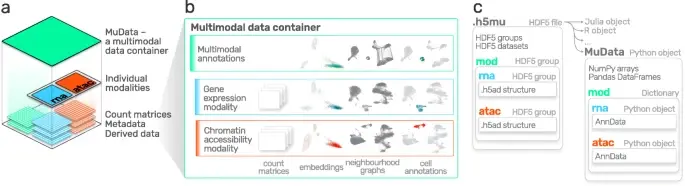
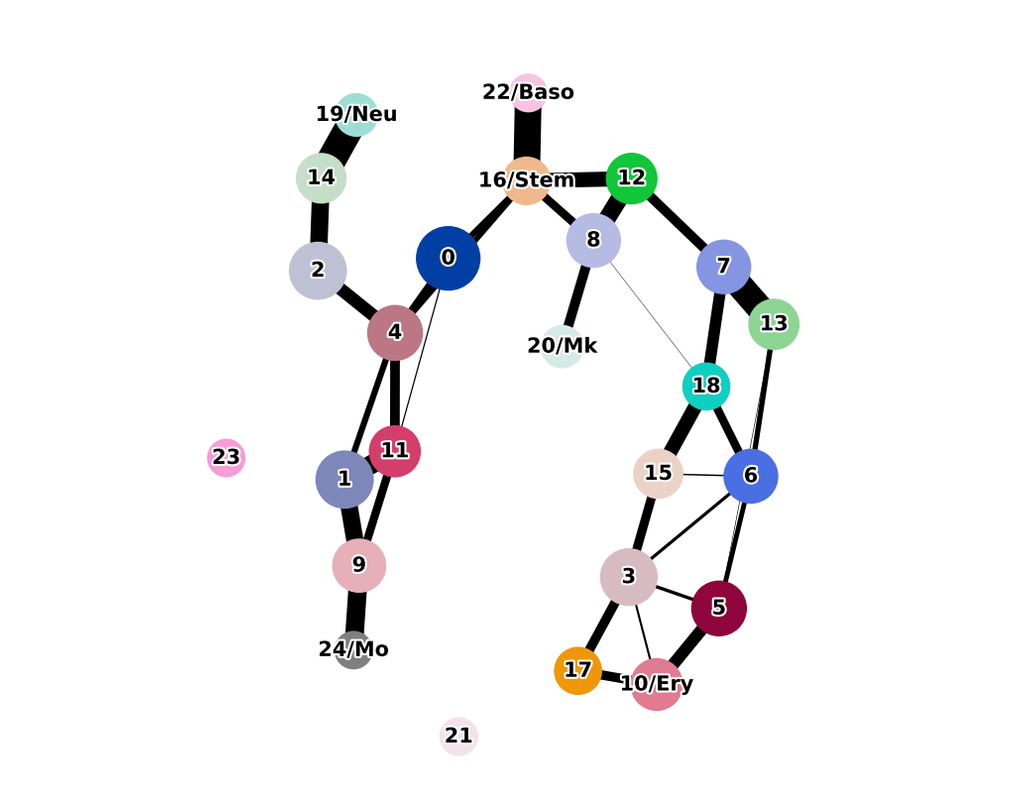
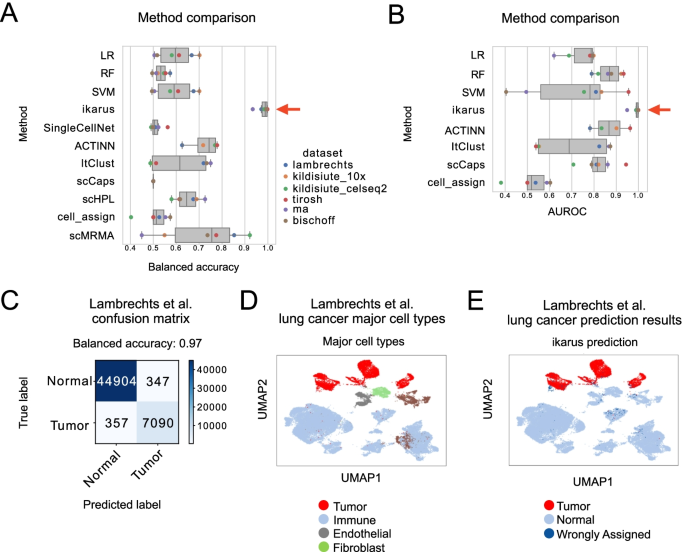
Notebooks
Premium
Trends
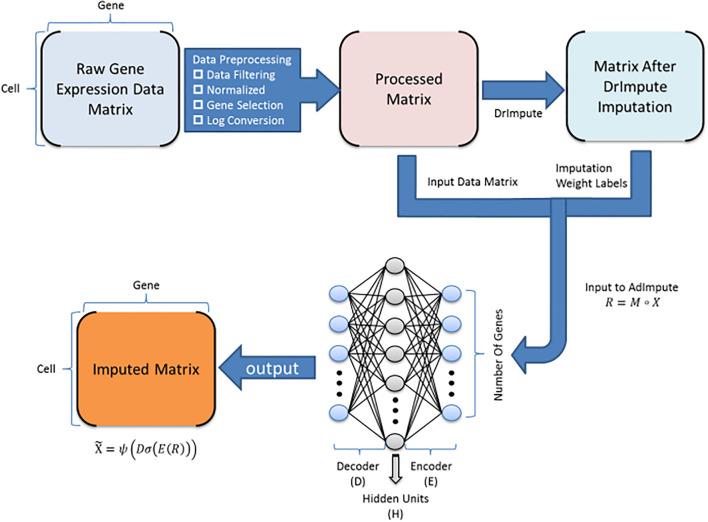
BioTuring
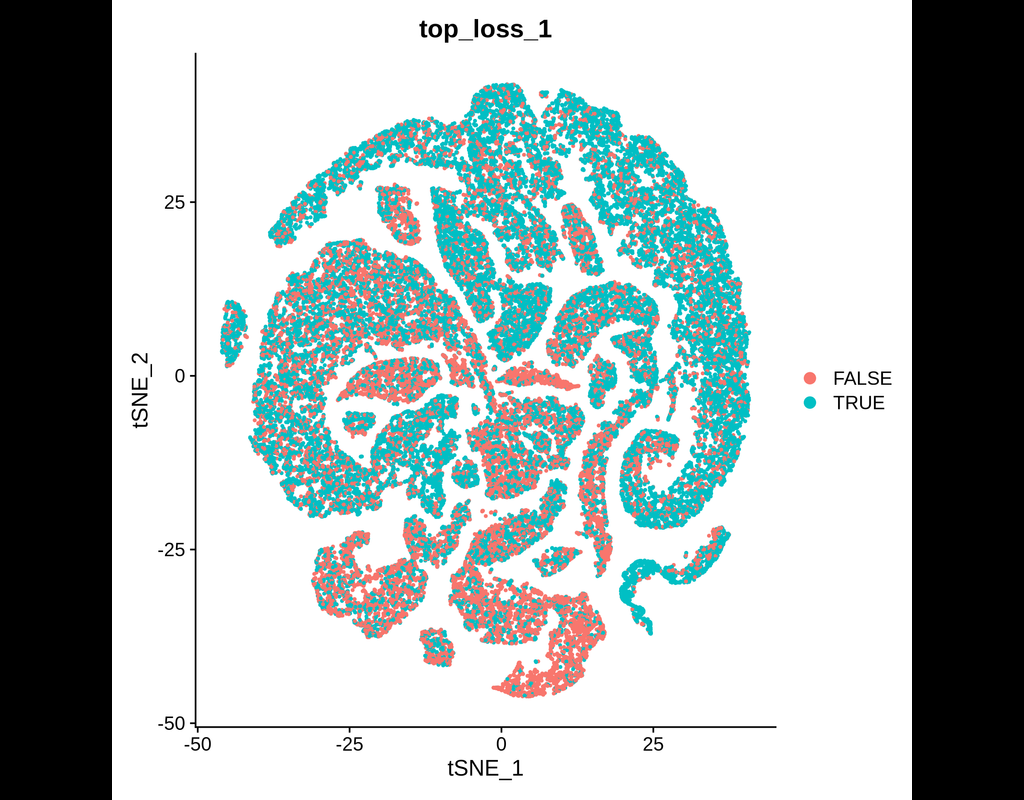
BioTuring
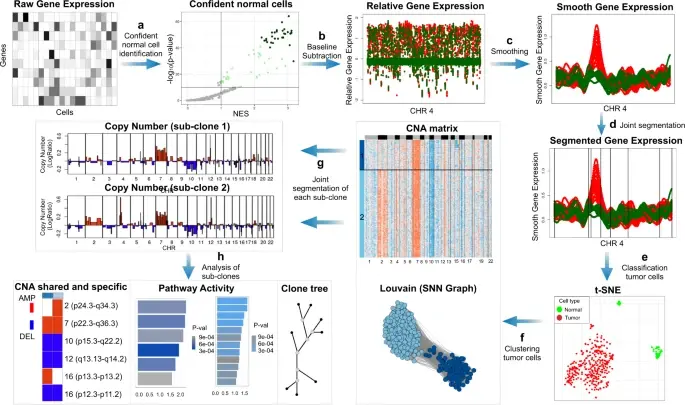
BioTuring
BioTuring
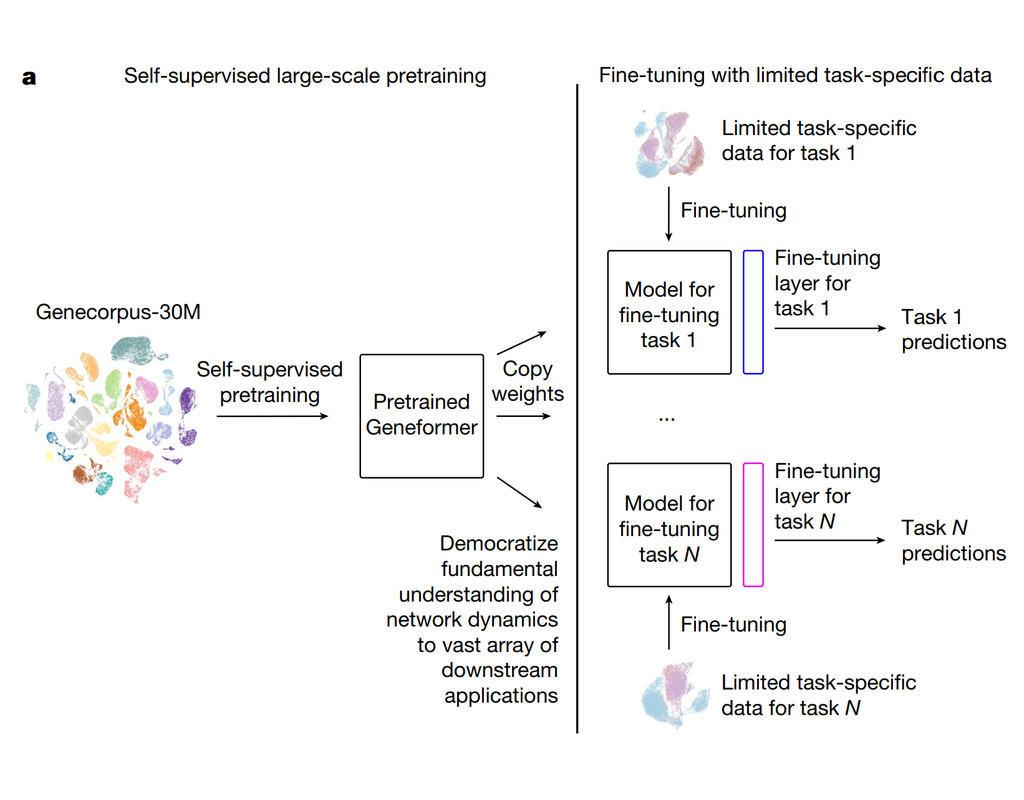
BioTuring
BioTuring
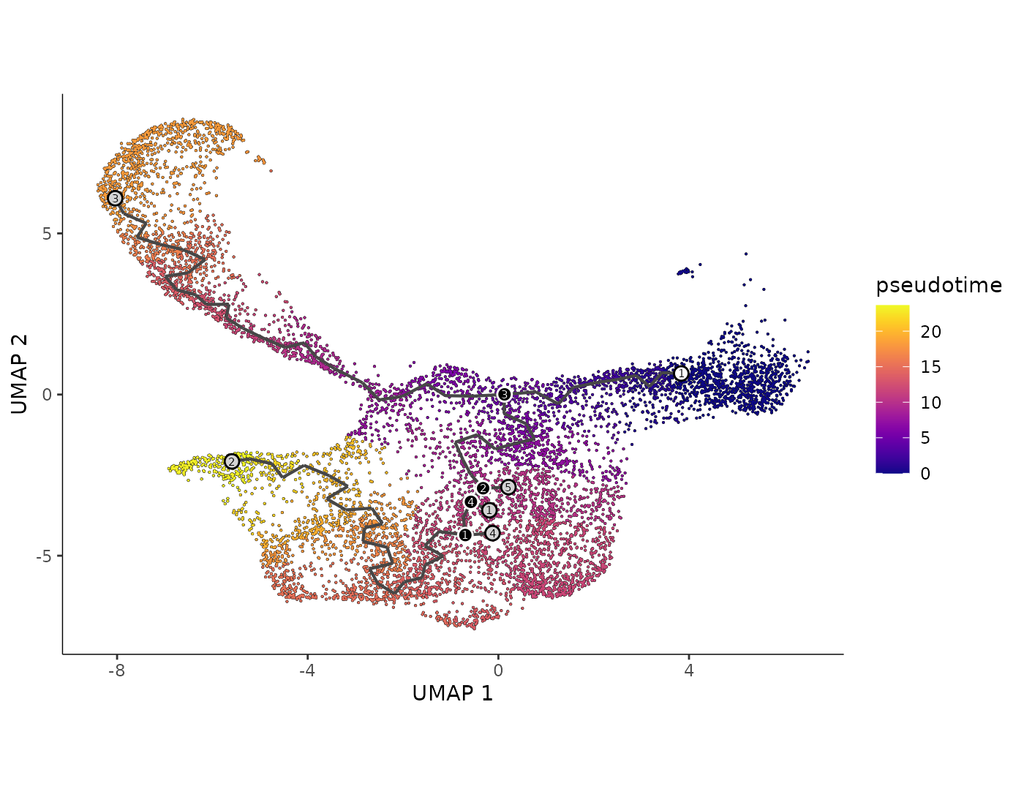
BioTuring
BioTuring
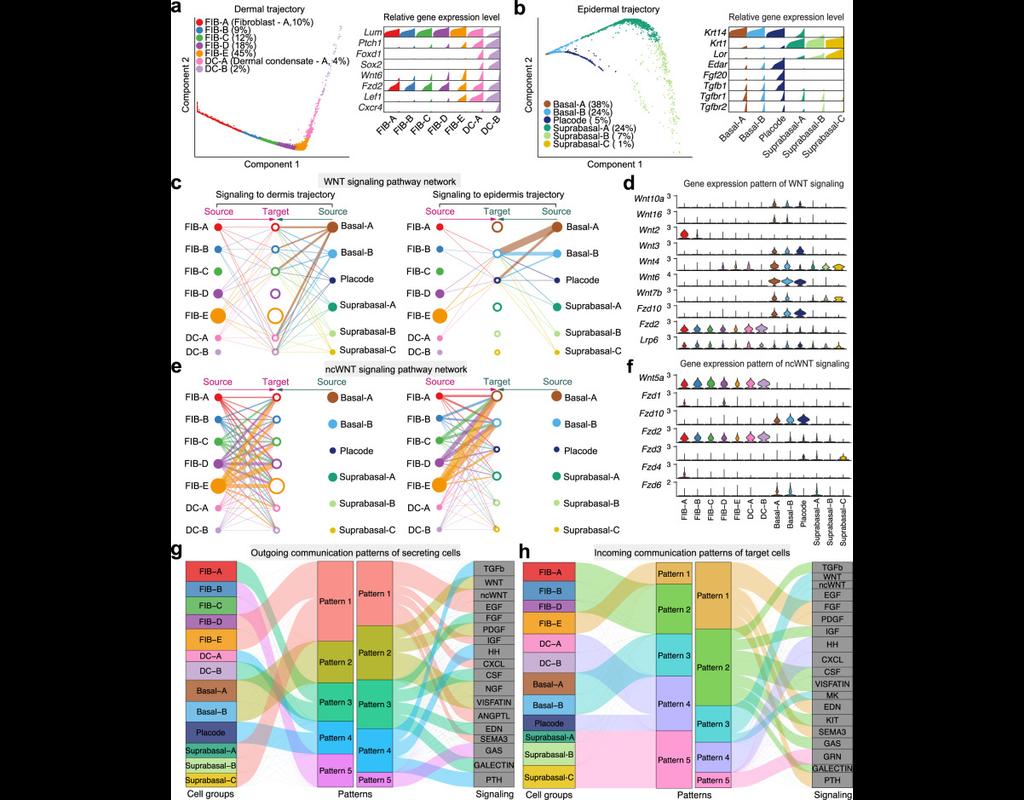
BioTuring
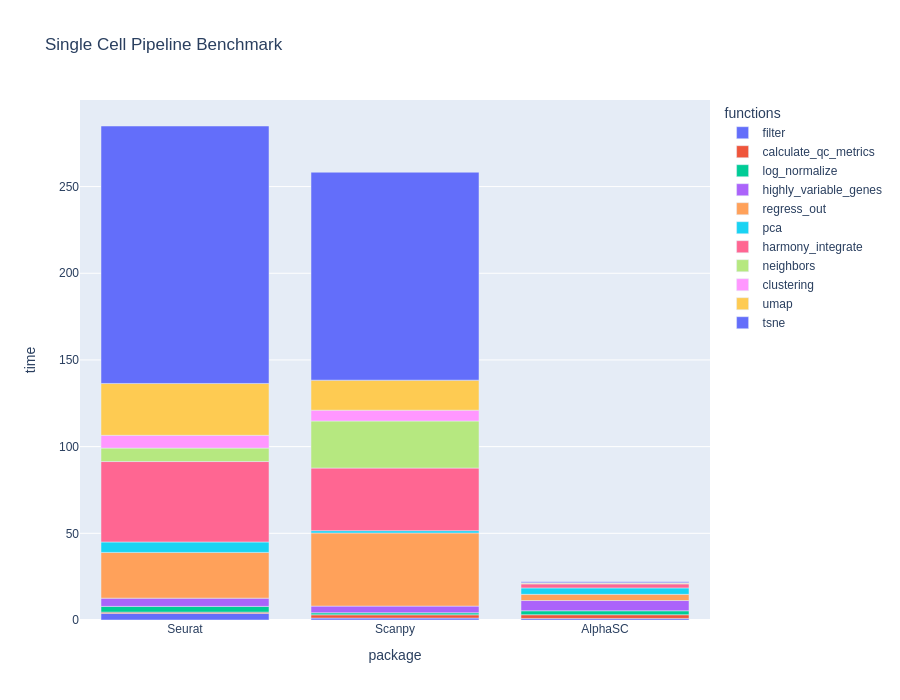
BioTuring
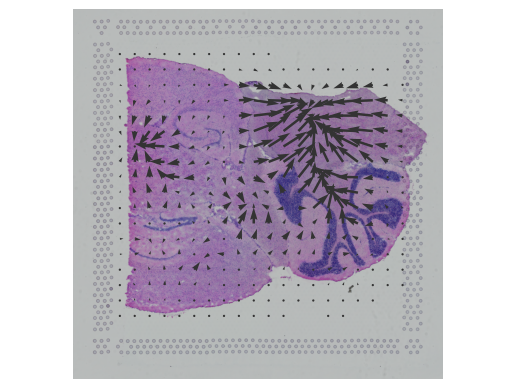
BioTuring
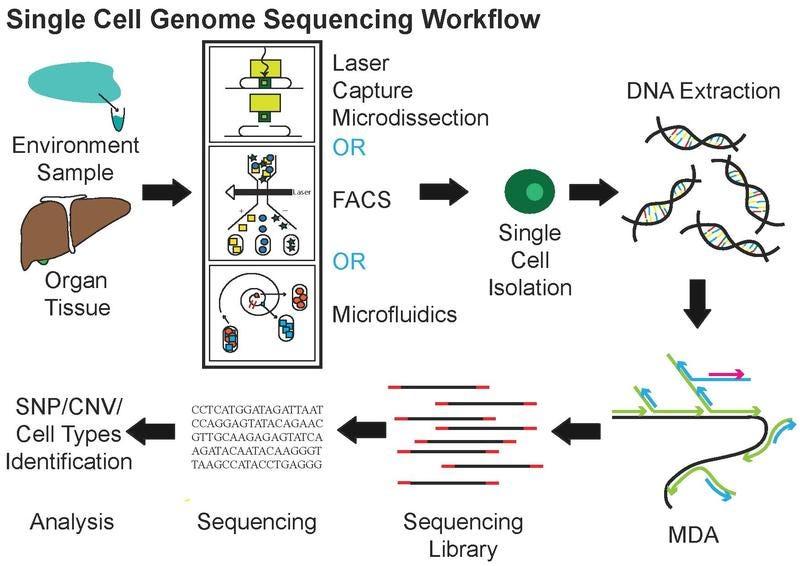
BioTuring

BioTuring
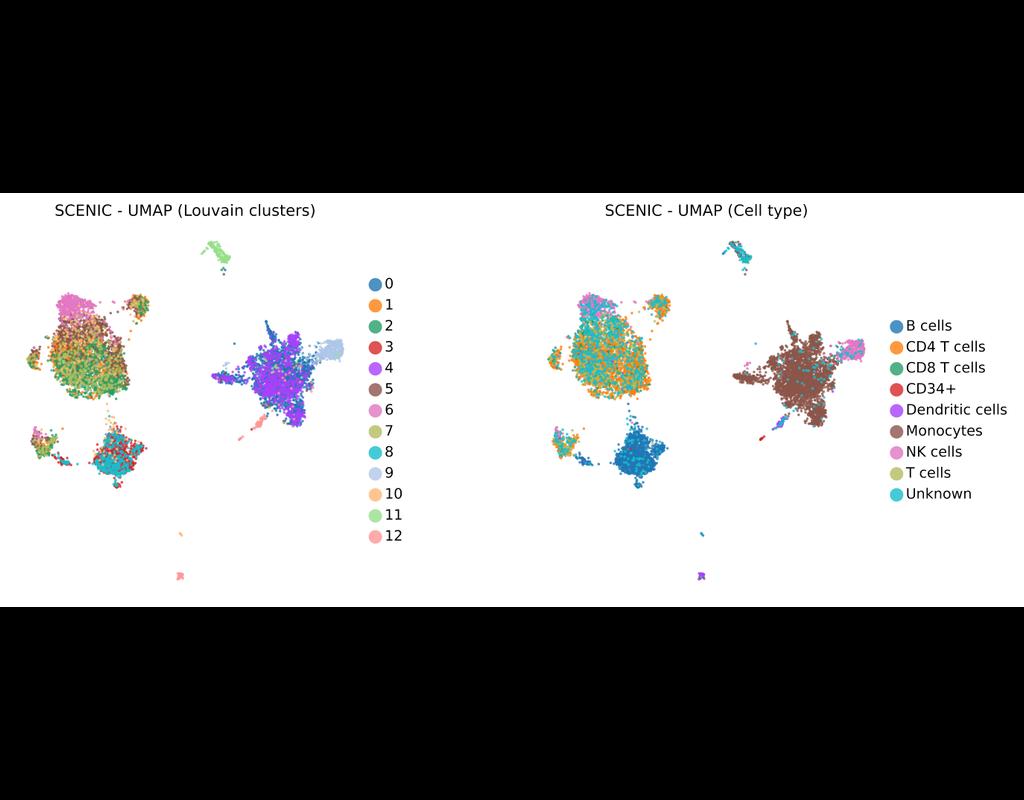
BioTuring
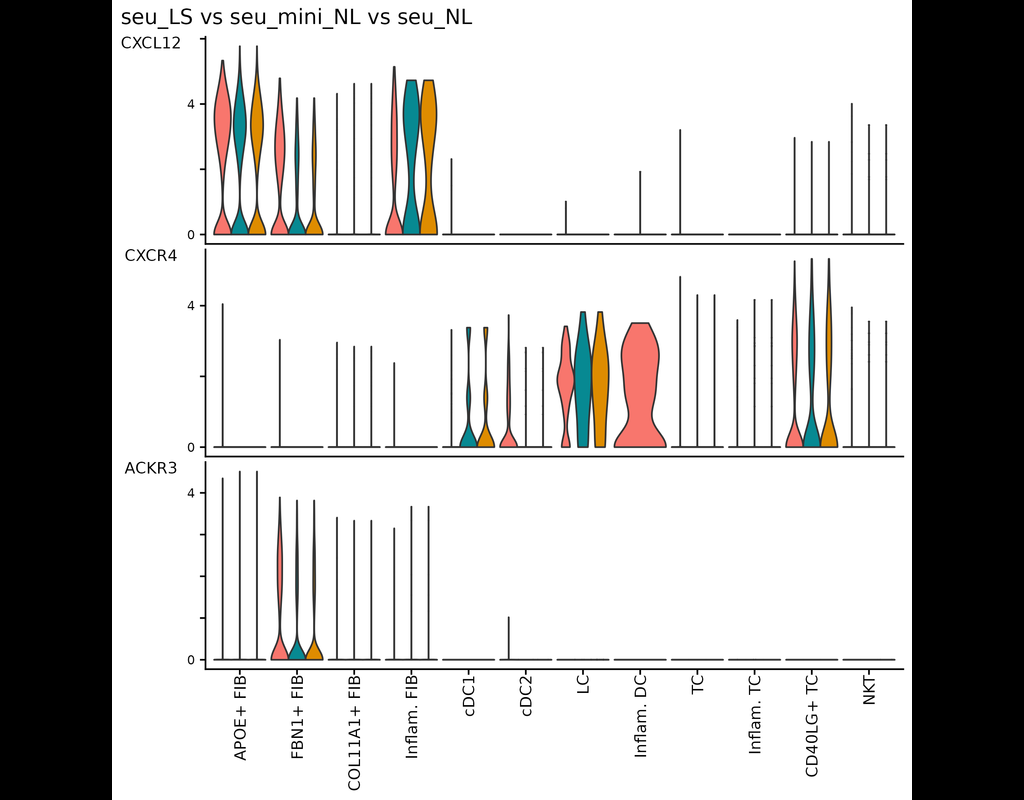
BioTuring
| Notebooks |
|---|